Risks of Contusions in Sports
Introduction to Concussions
Introduction to Concussions
Introduction to Concussions
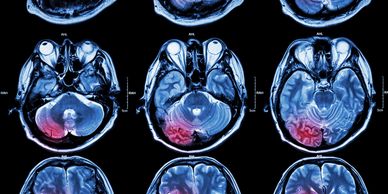
Concussions are common injuries that affect athletes at all levels, from amateurs to professionals. They occur due to direct impact on the body, causing damage to the underlying blood vessels and often resulting in bruising. While these injuries may seem minor, their impact can be significant, affecting both performance and long-term health of the athlete.
Common Causes of Concussions
Concussions can occur in any sport, but they are more prevalent in those involving physical contact or rapid movement.
Contact Sports:
Football and Rugby: In these sports, players are constantly at risk of receiving blows to various parts of the body due to tackles and collisions.
Hockey: Falls on the ice and contact with other players or the puck can result in concussions on any part of the body.
Non-Contact Sports:
Basketball: Poorly landed jumps can lead to contusions in the legs and hips, even without direct physical contact.
Cycling: Cyclists may experience concussions from falls or collisions, especially on rough terrain.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Introduction to Concussions
Introduction to Concussions

The symptoms of a concussion can vary depending on the severity of the injury.
Common symptoms include:
Localized Pain: A sensation of pain in the affected area, which can be sharp or dull.
Swelling: Inflammation at the site of impact, which may increase over time.
Bruising: A change in skin color indicating internal bleeding.
Limited Range of Motion: Mobility in the injured area may be restricted.
A proper diagnosis is crucial. Medical professionals typically conduct a physical examination and, if necessary, may request imaging such as ultrasounds or MRIs to assess the severity of the contusion.
Associated Risks of Contusions
Concussions are not just temporary annoyances; if not treated properly, they can lead to serious complications:
Chronic Injuries: Repeated concussions in the same area can lead to long-term damage to muscles or nerves.
Infections: In some cases, a severe contusion may open the door to infections, especially if the skin is broken.
Psychological Issues: Athletes who experience frequent injuries may develop anxiety or fear about returning to the sport, affecting their performance.
Role of Sports Medicine
Introduction to Concussions
Importance of Monitoring Medical Signals

What is Sports Medicine?
Sports medicine specializes in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of injuries related to sports. A team of professionals, including doctors, physical therapists, trainers, and nutritionists, works together to ensure the health and well-being of athletes.
Injury Prevention
Prevention is the most effective strategy for minimizing the risk of concussions and other injuries.
Prevention strategies include:
Education and Awareness: Training athletes on proper movement mechanics and the importance of warming up adequately to prepare muscles for exercise.
Physical Training: Designing training programs that strengthen muscles and improve flexibility and balance, thereby reducing the risk of injuries.
Proper Equipment: Utilizing appropriate gear (helmets, padding, proper footwear) to shield athletes from impacts.
Early Intervention and Treatment
When a concussion occurs, early intervention is essential:
RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation): This method helps reduce swelling and pain during the first 24 to 48 hours.
Medical Evaluations: Prompt medical attention can prevent further injury and guide the recovery process.
Personalized Rehabilitation: Physical therapists create rehabilitation programs tailored to each athlete’s condition and needs, focusing on restoring function and strength in the affected area.
Ongoing Education and Monitoring
Continuous education on health and injury prevention is crucial. Training programs for coaches and athletes on how to identify and respond to concussions can be extremely beneficial.
Importance of Monitoring Medical Signals
Importance of Monitoring Medical Signals
Importance of Monitoring Medical Signals

Regular Health Monitoring for Athletes
Monitoring the medical signals of each athlete is fundamental. This includes regular check-ups that evaluate various aspects of the athlete's health:
Cardiovascular Health: Monitoring heart performance to identify potential issues before they impact performance.
Flexibility and Muscle Strength: Regular assessments can detect weaknesses that predispose athletes to injuries.
Medical History: Keeping detailed records of previous injuries helps identify patterns and potential risks.
Benefits of Active Monitoring
Implementing a systematic approach to active monitoring offers multiple benefits:
Injury Prevention: Detecting changes in an athlete's physical condition that could lead to injuries.
Performance Improvement: Adjusting training programs based on the athlete's current physical state to maximize performance.
Safety in Competition: Ensuring athletes are in optimal condition to compete, thereby reducing the risk of injuries.
Conclusion
Importance of Monitoring Medical Signals
Conclusion
Concussions are an unavoidable aspect of sports, but their management and prevention are essential for athlete health. Sports medicine and monitoring of medical signals are critical tools in this process. By prioritizing the health and safety of athletes, we can maximize not only their performance but also their long-term well-being. Fostering a culture of care and prevention in the sports arena is key to ensuring that all athletes can enjoy their sports safely and effectively.
Copyright © 2024 RESPIRA INC - All rights reserved
This website uses cookies
We use cookies to personalise content and ads, to provide social media features and to analyse our traffic. We also share information about your use of our site with our social media, advertising and analytics partners who may combine it with other information that you've provided to them or that they've collected from your use of their.
